Zorora: Deep Research Engine
Zorora is a local-deployment deep research engine that searches across academic databases, web sources, and newsroom articles, then synthesizes findings with credibility scoring and citation graphs. Built for macOS (Apple Silicon) with minimal RAM footprint, meant to be run directly from your computer, with all content, outputs, and chats stored locally and not in the cloud, giving you complete control and privacy.
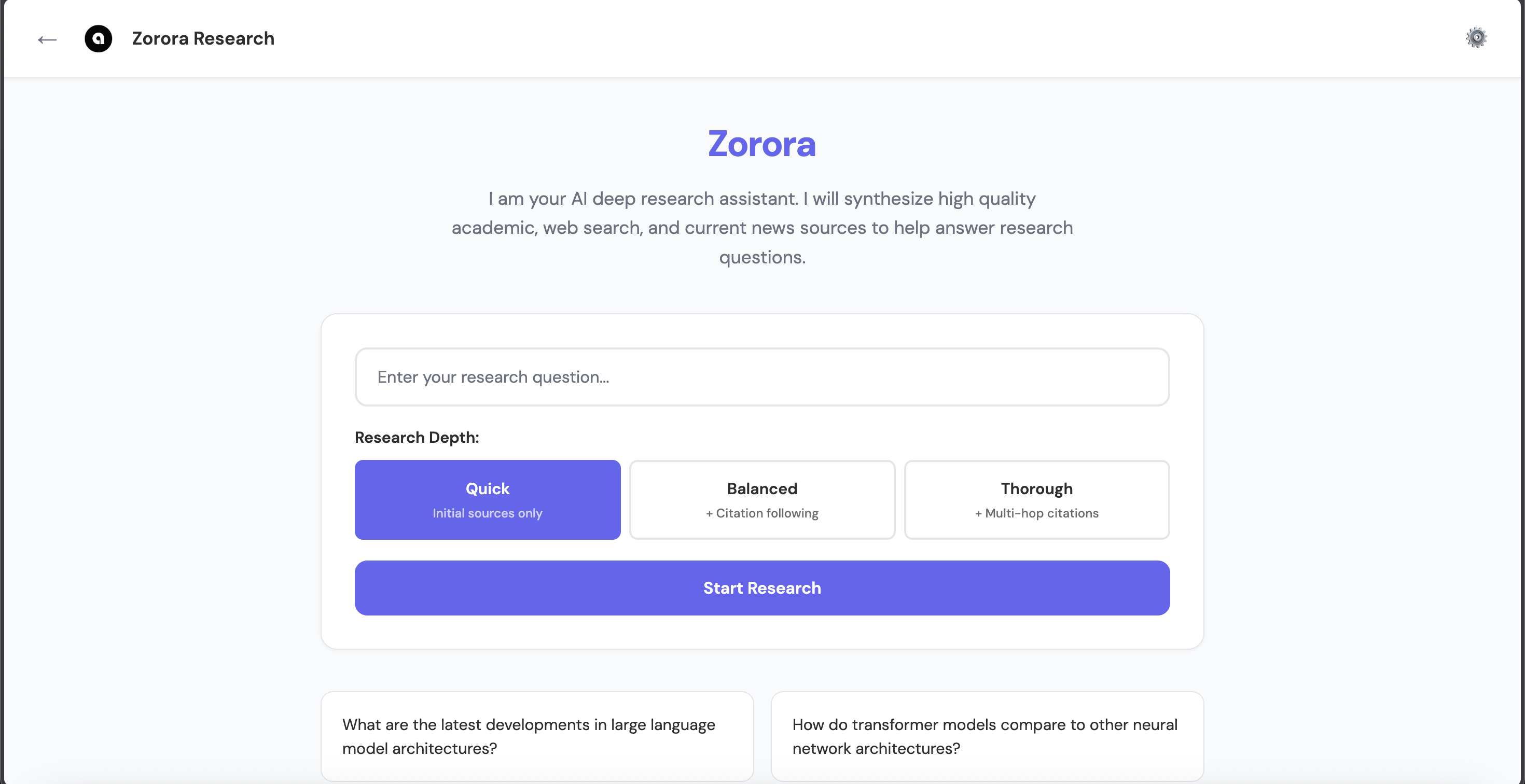
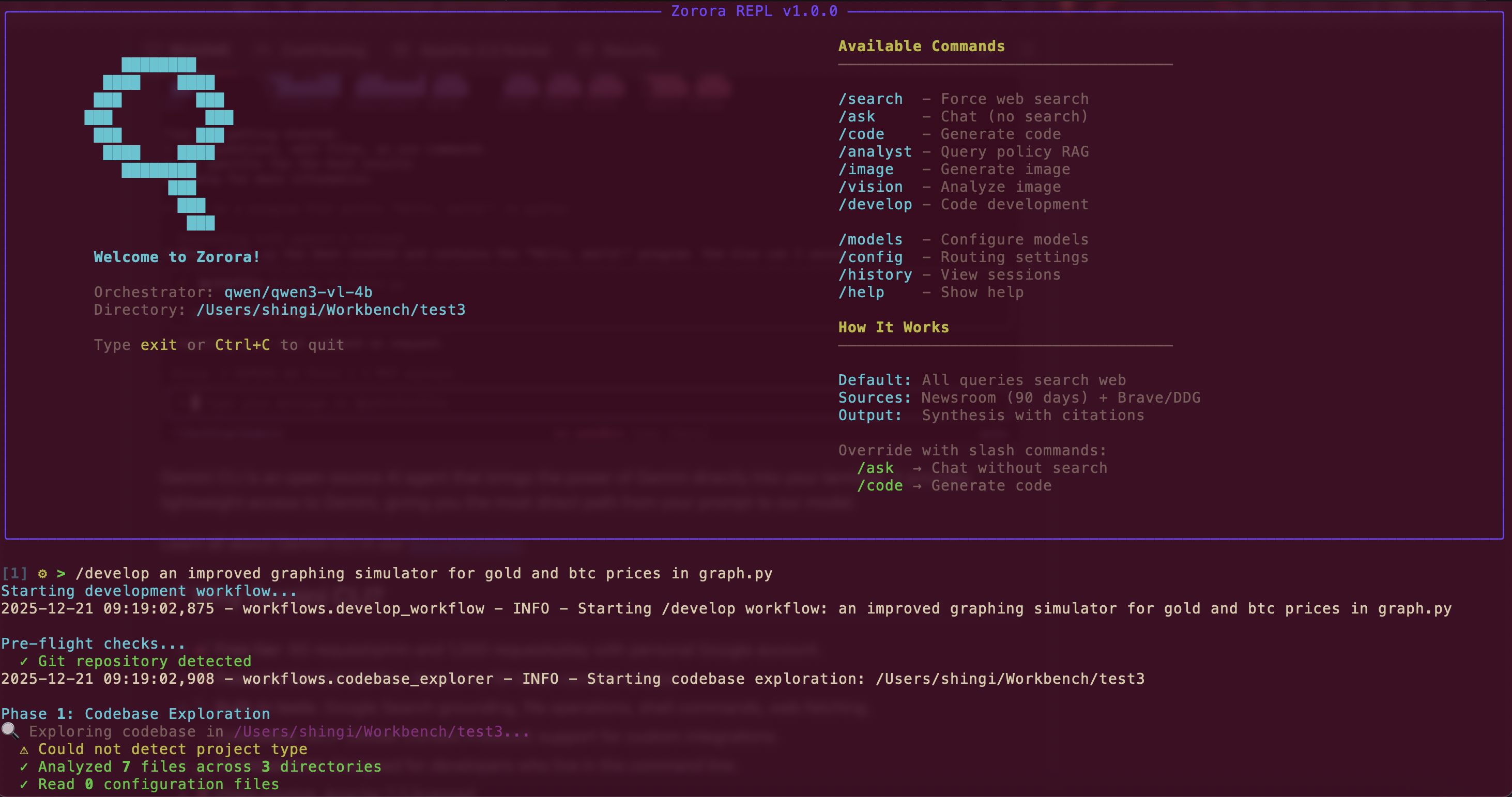
Zorora offers both Web UI and Terminal REPL interfaces
What is Zorora?
Zorora transforms from a basic research tool into a deep research engine that:
- Searches EVERYTHING - Academic databases (7 sources) + web search + Asoba newsroom
- Follows citation trails - Multi-hop research that explores cited papers
- Cross-references claims - Groups similar claims and counts agreement across sources
- Scores credibility - Transparent rules-based scoring of source authority
- Builds citation graphs - Visualizes relationships between sources
- Synthesizes with confidence - Generates comprehensive answers with citation levels
Core Value Proposition
Zorora provides:
- Complete Privacy - All processing and storage on your machine
- Local-First Architecture - Zero cloud dependencies (except source fetching)
- RAM Efficiency - Runs on MacBook Air M3 with 4B model (4-6 GB RAM)
- Dual Interfaces - Terminal REPL for engineers, Web UI for non-engineers
- Deterministic Reliability - Pattern-based routing (no LLM orchestration failures)
- Multi-Provider Support - Configure models from HuggingFace, OpenAI, and Anthropic APIs
Core Features
Deep Research Capabilities
6-Phase Research Pipeline:
- Parallel Source Aggregation - Searches academic (7 sources), web (Brave + DDG), and newsroom simultaneously
- Citation Following - Multi-hop exploration of cited papers (configurable depth: 1-3)
- Cross-Referencing - Groups claims by similarity and counts agreement
- Credibility Scoring - Rules-based scoring of source authority (academic journals, predatory publishers, retractions)
- Citation Graph Building - Constructs directed graphs showing source relationships
- Synthesis - Generates comprehensive answers with confidence levels and citations
Research Depth Levels:
- Quick - Initial sources only (skips citation following, depth=1, ~25-35s)
- Balanced - Adds citation following (1 hop, depth=2, ~35-50s) - Coming soon
- Thorough - Multi-hop citation exploration (up to 3 levels deep, depth=3, ~50-70s) - Coming soon
Additional Features
- Research persistence - Save/load findings with metadata
- Code generation - Dedicated Codestral model for coding tasks
- Multi-step development -
/developworkflow: explore → plan → approve → execute → lint - Slash commands - Force workflows:
/search,/ask,/code,/develop,/image,/vision - Deterministic routing - Pattern-based decision tree (no LLM routing failures)
- Hybrid deployment - Local 4B orchestrator + remote 32B specialists
- RAM-efficient - Runs on MacBook Air M3 with 4B model
- Dual interfaces - Terminal REPL for engineers, Web UI for non-engineers
- Multi-provider support - Configure models from HuggingFace, OpenAI, and Anthropic APIs
- Visual settings management - Web UI settings modal for easy configuration
- Vision and image generation - Dedicated models for image analysis and text-to-image generation
Architecture
Zorora uses deterministic routing with pattern matching instead of LLM-based orchestration. This design choice enables reliable operation with small 4B models while maintaining RAM efficiency.
Design Philosophy
- Deterministic over clever - Code-controlled workflows, not LLM orchestration
- Research-first - Optimized for multi-source synthesis and citation management
- RAM-efficient - Runs on MacBook Air with 4B orchestrator model
- Persistent knowledge - Save and retrieve research findings locally
- Simple and reliable - Hardcoded pipelines that just work
Architecture Diagram
User Query / Slash Command / Web UI Request
↓
Pattern Matching (simplified_router.py) / Flask Routes (ui/web/app.py)
↓
├─→ DEEP RESEARCH WORKFLOW (6-phase pipeline)
│ ├─► Phase 1: Parallel Source Aggregation
│ │ ├─► Academic (7 sources: Scholar, PubMed, CORE, arXiv, bioRxiv, medRxiv, PMC)
│ │ ├─► Web (Brave Search + DuckDuckGo)
│ │ └─► Newsroom (Asoba API)
│ ├─► Phase 2: Citation Following (configurable depth: 1-3)
│ ├─► Phase 3: Cross-Referencing (groups claims by similarity)
│ ├─► Phase 4: Credibility Scoring (rules-based)
│ ├─► Phase 5: Citation Graph Building
│ └─► Phase 6: Synthesis (Reasoning Model)
├─→ CODE WORKFLOW (Codestral specialist)
├─→ DEVELOPMENT WORKFLOW (/develop - multi-step)
├─→ FILE OPERATIONS (save/load/list)
├─→ IMAGE WORKFLOWS (generate/analyze)
└─→ SIMPLE Q&A (/ask - direct model)
Key Principles
- No LLM-based orchestration - Patterns determine routing, code controls execution
- Hardcoded workflows - Fixed pipelines for predictable results
- Persistent research - Everything saved to
~/.zorora/research/with metadata - Specialist models - Codestral for code, reasoning model for synthesis, vision for images
- Multi-provider support - Configure models from LM Studio (local), HuggingFace, OpenAI, and Anthropic APIs
- Visual configuration - Web UI settings modal for easy model/endpoint management
- Hybrid inference - Mix local models (4B orchestrator) with remote HuggingFace endpoints (32B Codestral)
Core Components
1. Simplified Router (simplified_router.py)
Uses pattern matching to route queries to workflows. No LLM involved - pure pattern matching ensures consistent, fast routing (0ms decision time).
2. Research Engine (engine/research_engine.py)
High-level interface for deep research:
- Starting research
- Loading past research
- Searching research history
- Executing deep research workflow
3. Deep Research Workflow (workflows/deep_research/)
Hardcoded pipeline for multi-source research:
aggregator.py- Source aggregationcredibility.py- Credibility scoringsynthesizer.py- Synthesis generationworkflow.py- Workflow orchestrator
4. Storage Layer (engine/storage.py)
Local-first storage:
- SQLite database (
~/.zorora/zorora.db) for fast indexed queries - JSON files (
~/.zorora/research/findings/) for full research state
5. Web UI (ui/web/app.py)
Flask-based web interface:
- Research query interface with depth selection
- Settings modal for configuration
- Research results display with synthesis, sources, and credibility scores
Local-First Design
Storage Architecture
Research Request
↓
ResearchEngine.deep_research()
↓
DeepResearchWorkflow.execute()
↓
LocalStorage.save_research()
├─► SQLite Index (~/.zorora/zorora.db)
│ ├─► research_findings (metadata)
│ ├─► sources (indexed)
│ └─► citations (graph)
└─► JSON Files (~/.zorora/research/findings/<id>.json)
└─► Full research state (sources, findings, synthesis)
Privacy & Control
- All processing on your machine - No cloud computation
- Local storage only - Research data never leaves your machine
- Zero cloud dependencies - Except source fetching (academic databases, web search)
- Complete control - You own all data, all outputs, all chats
Performance
- Routing decision: 0ms (pattern matching, no LLM)
- Research workflow: Varies by depth
- Quick (depth=1): ~25-35s
- Balanced (depth=2): ~35-50s - Coming soon
- Thorough (depth=3): ~50-70s - Coming soon
- Storage queries: <100ms (SQLite indexed)
- Code generation: 10-90 seconds (local: 10-30s, HF 32B: 60-90s)
- RAM usage: 4-6 GB (4B orchestrator model)
Why This Architecture?
Problem: 4B Models Can’t Orchestrate
Traditional multi-model orchestration requires the LLM to:
- Generate valid JSON plans
- Make routing decisions
- Handle multi-step iteration
- Recover from tool failures
4B models fail at all of these. They can’t reliably generate JSON, struggle with function calling, and get stuck in loops.
Solution: Code Handles Complexity
Instead of asking the 4B model to be smart, we made the code smart:
- Pattern matching routes queries (no LLM decision)
- Hardcoded workflows execute pipelines (no LLM planning)
- Fixed iteration count (no LLM loop detection)
- Deterministic error handling (no LLM recovery)
Result: 100% reliability with 4B models, 1/3 the RAM usage of 8B orchestrators, complete privacy with local storage.
Trade-offs
What we lost:
- Flexibility for complex multi-tool queries
- LLM creativity in tool selection
- Adaptive workflows based on results
What we gained:
- 100% routing reliability (pattern matching never fails)
- Predictable behavior (same query = same workflow)
- RAM efficiency (4B model = 4-6 GB vs 8B = 12-16 GB)
- Simple debugging (no “why did it choose that tool?”)
- Fast responses (no LLM routing overhead)
Quick Start
Installation
Or install from GitHub:
pip install git+https://github.com/AsobaCloud/zorora.git
Run Your First Query
Terminal:
zorora
[1] ⚙ > What are the latest developments in large language model architectures?
Web UI:
zorora web
# Opens at http://localhost:5000
API:
from engine.research_engine import ResearchEngine
engine = ResearchEngine()
state = engine.deep_research("Your research question", depth=1)
print(state.synthesis)
Next Steps
- Getting Started - Installation and configuration guide
- Guides - Comprehensive guides for all features
- API Reference - Programmatic access documentation
- Technical Concepts - Deep dive into architecture
- Use Cases - Real-world examples
See Also
- Architecture Documentation - Detailed architecture explanation
- Research Pipeline - How the 6-phase pipeline works
- Storage Design - Local-first storage architecture
- Routing Mechanism - Deterministic pattern matching
