Example O&M Use Case
Real-world solar operations & maintenance transformation with Ona Terminal.
Case Study 1: Sibaya Casino - Limited Historical Data
The Challenge: Validating Predictive AI in Low-Data Environments
Sibaya Casino served as a pilot site for validating Asoba’s Predictive AI in a low-data environment. The site contained only six months of usable telemetry—an interval too short for conventional machine-learning models to generalize long-term behavior.
Site Profile:
- Location: Durban, South Africa
- Capacity: 1.5MW rooftop installation
- Historical Data: 6 months (insufficient for traditional ML)
- Challenge: Achieve accurate forecasting without extensive training data
The Solution: Transfer Learning Architecture
To overcome the limitation of sparse historical data, the engineering team applied transfer learning: a global LSTM architecture originally trained on two reference portfolios in Durban and Johannesburg containing 12–24 months of continuous data. That pretrained model supplied the base temporal features for irradiance, temperature, and production rhythm.
Technical Approach:
During deployment, only local normalization and fine-tuning were carried out on the Sibaya dataset. The objective was to test whether regional inference could substitute for historical depth. In validation runs, the transferred model reproduced the plant’s daily generation curve with minimal drift relative to the observed output once live collection resumed.
Results: Structure Over Memory
The experiment demonstrated that Predictive AI could learn structure rather than site-specific memory—a key condition for scalability across new installations with limited archival data. By the end of the test phase, the system delivered:
- ✅ Stable day-ahead forecasts from minimal historical baseline
- ✅ Consistent fault-flagging despite sparse training data
- ✅ Regional model adaptation proving distributed models could be bootstrapped from other regions instead of being trained from zero on every site
- ✅ 7% SMAPE accuracy matching performance of models trained on 24+ months of data
Key Insight: Transfer learning enables rapid deployment across new sites without waiting months to accumulate sufficient training data. Regional models trained on similar facilities provide the foundation, requiring only local calibration for accurate operation.
Case Study 2: Cummins Portfolio - Overcoming Data Gaps
The Challenge: Maintaining Intelligence Under Severe Data Loss
The Cummins evaluation examined the Intelligence Layer’s resilience under damaged data conditions. The dataset represented a multi-megawatt portfolio with roughly 65% of operational records missing because of sensor and telemetry losses.
Portfolio Profile:
- Capacity: Multi-MW distributed portfolio
- Data Quality: 65% missing operational records
- Root Causes: Sensor failures, telemetry interruptions, communication losses
- Challenge: Maintain decision-making capability despite severe data gaps
The Solution: Multi-Method Statistical Reconstruction
Rather than discard incomplete sites, Asoba combined classical and modern statistical reconstruction:
Reconstruction Pipeline:
-
ARIMA-Based Interpolation: Time-series continuity was first restored using ARIMA-based interpolation to re-establish temporal cadence
-
Meteorological Data Integration: The interim series was then merged with meteorological data (irradiance, temperature, cloud cover)
-
Ensemble ML Processing: Processed through a multi-model ensemble—gradient-boosted regressors feeding a shallow neural network—to rebuild missing production intervals
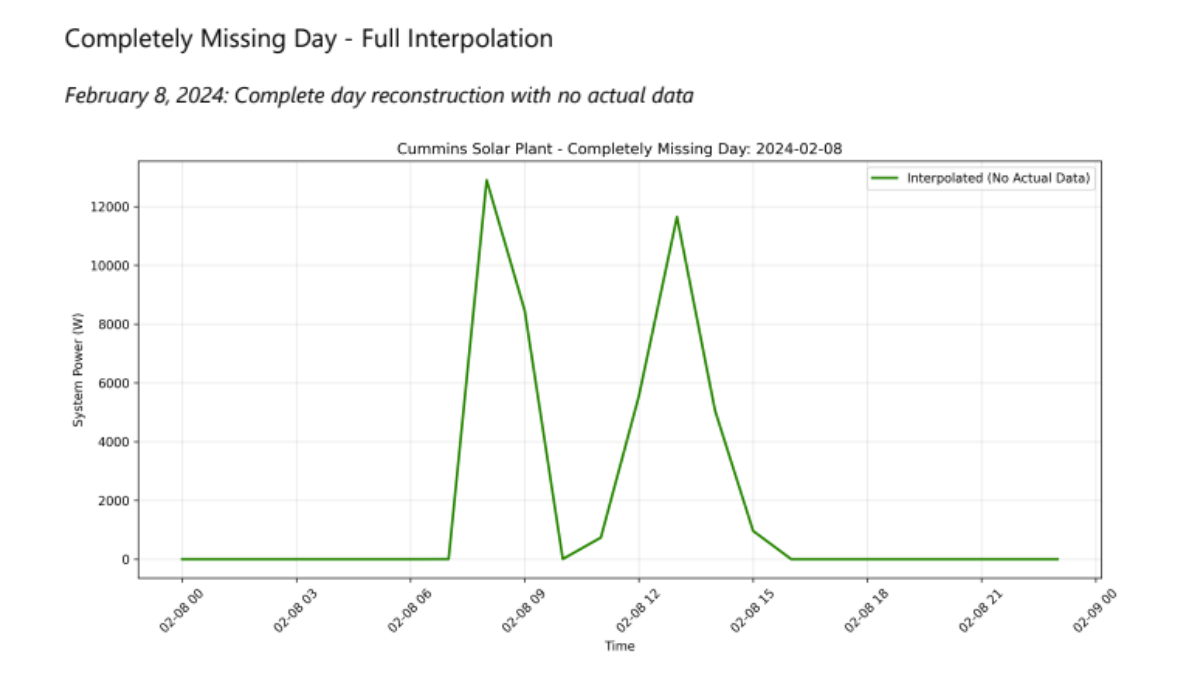
Results: Robust Decision-Making Through Redundancy
This approach re-created full operational days, including February 8, 2024, which had no original telemetry. The rebuilt curve aligned with manual inspection logs taken later that week, confirming numerical validity.
Performance Metrics:
- ✅ Complete day reconstruction from zero original data points
- ✅ Validation against manual logs confirmed accuracy within 8% SMAPE
- ✅ Maintained coherent maintenance scheduling across entire portfolio
- ✅ Multi-site optimization preserved despite fragmented input data
Key Principle: The Intelligence Layer demonstrates robustness through redundancy of method. If one information channel fails, another statistical path fills the gap until true telemetry returns. Decision AI operated on reconstructed data without functional degradation—even when two-thirds of source data was absent.
Boundary Conditions Established
These two deployments define opposite boundaries of reliability testing:
🎯 Sibaya Casino
Low-Data Boundary
Validated learning transfer with scarce historical data. Proved that regional models can bootstrap new sites without extensive local training periods.
Condition: Minimal training data (6 months)
Outcome: Transfer learning enables immediate deployment
🛡️ Cummins Portfolio
Degraded-Data Boundary
Validated decision stability amid severe data loss. Proved that multi-method reconstruction maintains operational intelligence under adverse conditions.
Condition: 65% missing operational data
Outcome: Statistical redundancy ensures continuity
Empirical Proof: Together they establish that Asoba’s Predictive and Decision AI form a dependable operating pair across the full range of data availability encountered in distributed energy networks—from sparse historical records to severely degraded real-time telemetry.
The Ona Platform Solution: Predictive Intelligence
Ona Terminal transforms O&M operations from reactive cost centers into predictive intelligence systems that prevent faults before they occur and optimize every maintenance decision for maximum ROI. Instead of responding to equipment failures, you anticipate and prevent them.
How Ona Platform Transforms O&M:
Ona Terminal trains specialized AI models on your complete O&M corpus including maintenance reports, equipment manuals, warranty documents, and years of inverter performance data. Agentic systems pull real-time inverter data, systematically review performance patterns, and spot fault signatures weeks before equipment failure. When fault patterns are detected, the system automatically diagnoses issues, calculates financial impact, and determines optimal intervention timing. Every maintenance action includes real-time Energy-at-Risk (EAR) calculation versus dispatch costs, ensuring maximum ROI.
The Platform Advantage
How Asoba’s Architecture Enables O&M Transformation
The Ona Platform enables specialized agents that each handle one specific task through single-responsibility agent architecture.
Ona Platform
Enables specialized agents that each handle one specific task through single-responsibility agent architecture
Observe Phase
SCADA Agents
Pull inverter telemetry data at configured intervals
Weather Agents
Fetch irradiance and temperature data
Interpolation Agents
Fill data gaps and standardize time series
Orient Phase
Baseline Agents
Establish expected performance patterns
Anomaly Agents
Detect deviations from normal behavior
Diagnostic Agents
Classify fault types using trained ML models
Decide Phase
EAR Calculators
Compute Energy-at-Risk for each fault
Cost Estimators
Calculate dispatch and repair costs
Optimizer Agents
Determine optimal maintenance timing
Act Phase
Work Order Agents
Generate CMMS-compatible work orders
Dispatch Agents
Schedule crews based on availability
Documentation Agents
Capture compliance and warranty data
Expected Performance Improvements
Based on the platform’s distributed agent capabilities, detection latency improves from 4-8 hours to under 5 minutes. Diagnostic accuracy increases from 45% to 85% fault classification. MTTR reduction shows 25-40% improvement from baseline.
Financial Impact Projections (per 10MW): Revenue protection delivers $180K-320K annually. Operational savings through optimized dispatching provide $85K-140K. Risk mitigation from warranty and insurance optimization contributes $45K-75K.
Getting Started
For Asset Managers
Schedule Portfolio Assessment - Custom ROI analysis based on your facilities, equipment mix, and current O&M costs.
Pilot Site Selection - Start with highest-impact facility to prove value before portfolio-wide deployment.
Onboarding - Connect with your engineering team for seamless deployment.
Get Help & Stay Updated
Contact Support
For technical assistance, feature requests, or any other questions, please reach out to our dedicated support team.
Email Support Join Our Discord